Adaptable photovoltaic generation solution for use in buildings and distributed generation
Data
Acronym: AISOVOL2
Reference: RTC2019-006994-3
Partners: Instituto Tecnológico y de Energías Renovables (ITER) and Centro Nacional de Energías Renovables (CENER).
Duration: 06/01/2020 – 12/3112/2023
Budget: 768,516.50 €
Co-Financing: Challenges Collaboration 2019. State Programme for R&D&I Oriented towards the Challenges of Society. Ministry of Science and Innovation.

Project overview
The future of photovoltaic energy is considered to lie in the integration of this technology in buildings, which is currently a growing market, with an expected penetration rate of 13% by 2022. In this way, photovoltaic stands out as a technology that will play a key role in the urban and environmental development of cities, driving the construction or adaptation of so-called near-zero energy buildings.
In response to this market trend and the objectives set in the energy sector, both national and European, the AISOVOL2 project, a photovoltaic generation solution for use in buildings and distributed generation, is being developed. This project aims to respond to the need for innovative photovoltaic solutions that allow a more intensive and multifunctional use of the available surface area in buildings, achieving sustainable cities.
The main objective of the project is the development and manufacture of an adaptable and multi-purpose photovoltaic module, which increases the architectural resources available for both building-adapted photovoltaic technology and technology integrated into the building structure itself, using cutting-edge materials and the latest photovoltaic technology, such as bifacial cells. This will allow for the evolution of research into alternatives that meet the trends in the photovoltaic market and the requirements of professionals in the construction industry.

This company is also a continuation of the line of research undertaken with the AISOVOL Project, which proposed the manufacture of a modular photovoltaic module that could be integrated and easily adapted for use as an architectural element by replacing some of the components that make up a conventional photovoltaic module, the most notable modification being the replacement of tempered glass with compact polycarbonate.
In AISOVOL2, alternatives are introduced in the design of the photovoltaic module that make it possible to overcome the difficulties encountered during the first project, based on the experience acquired during its execution. The alternative materials proposed respect the character of the previous project in terms of the features of the photovoltaic module to be manufactured and give this proposal an innovative nature, taking advantage of the development of new cutting-edge materials specially designed for the photovoltaic sector and the latest market trends, bifacial technology.
It also includes carrying out the necessary tests that commercial products of this technology must pass. Specifically, compliance with the standards for crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules established by IEC 61215 in terms of design qualification and approval will be verified. In this way, the viable products obtained with this experience will be suitable for commercialisation.
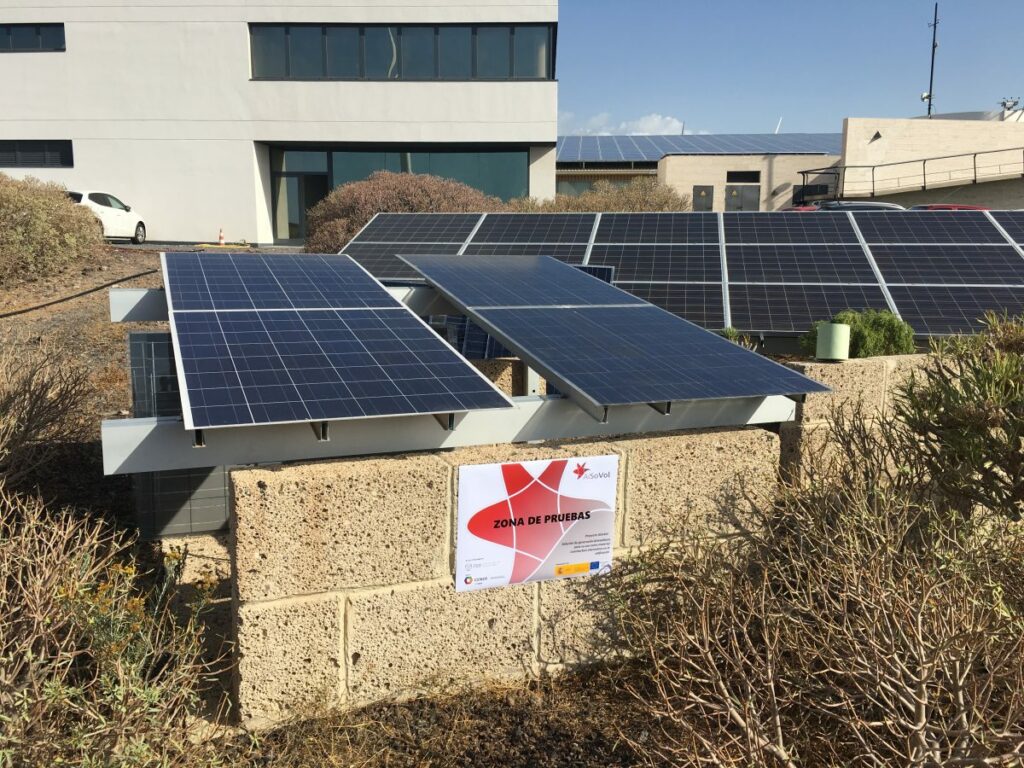
On the other hand, the project is completed with the design and manufacture of a monitoring and recording system for the characterisation and qualification of photovoltaic modules by means of field tests. This system will complement the work carried out in the previous AISOVOL project, which did not include field tests, and makes it possible to compare the performance of the two designs.
Similarly, it will allow a study of the performance of bifacial modules to assess the influence of certain installation parameters, such as mounting height, tilt or ground reflectivity. Thus, the objective of the monitoring system is to obtain information on the practical performance of the module during real daily operation, with changing irradiance and temperature conditions, usually very different from those established in the measurement standards for this technology. Likewise, thanks to the continuous determination of the IV characteristic curve of the photovoltaic modules by this system, it will be possible to detect various types of problems in the panel elements, such as an excessive internal resistance or a group of defective cells.